Are you considering trying out one of the many new generative AI tools? The potential rewards are compelling, but it's essential to understand the basics of generative AI and the risks to avoid when incorporating it into your business.
Is Generative AI Right for Your Business?
AI can help businesses improve decision-making, enhance customer experience, increase productivity, better manage risks, and realize new revenue opportunities. No doubt, the potential rewards are compelling. A 2023 Lucidworks study reports
"…global companies are gearing up for an investment surge, with an impressive 93% planning to increase their AI spending in the next 12 months.”
You might not know that many AI initiatives fail when organizations don't prepare properly. After all, AI isn't magic. But AI is a game-changer for companies that prepare and strategically incorporate AI into their workplace.
This guide covers the basics of generative AI and the risks to avoid when incorporating it into your business. Learn how to successfully adopt Generative AI technology and make it a competitive advantage. Hint: Artificial Intelligence is better with Information Architecture.
What Is Generative AI and How Does It Work?
Generative AI, or GenAI, is a machine learning application that creates unique content based on training data. That training consists of publicly available information on the web – for example, Common Crawl, OpenAI’s WebTexts, books, and Wikipedia – ingested into a sophisticated algorithm. The algorithm is called a Large Language Model (LLM).
LLMs, which learn words, concepts, and term relationships in everyday language, emulate a human-level understanding of questions and respond with well-written, plausible answers.
The best part is that it's versatile. We’re seeing GenAI used for marketing, advertising, and campaign copy, outlines for reports or documents, form letters, job descriptions, resumes, cover letters, stories, scripts, and even books!
We used an LLM to generate an outline for this very blog post. Think about that for a minute. A GenAI application like ChatGPT creates new content. ChatGPT isn't retrieving a copy of the information. It's using a GPT LLM to generate brand new content, much like a human would author new content.
The most significant benefit of LLMs in the workplace might be accessing existing corporate knowledge and communicating information in easy-to-understand language. This approach is referred to as retrieval-augmented generation or RAG. RAG can speed up information flows throughout the enterprise and provide value in every department and function. We’ll come back to RAG shortly.
Potential Risks of Incorporating Generative AI into Business Operations
While AI has the potential to drive significant benefits, such as increased efficiency and productivity, it introduces new risks and challenges. Don't worry; there are ways to mitigate these risks. So, let’s dig into the risks and how to avoid them.
AI doesn't understand anything, unlike humans. It learns language patterns and uses complex math to predict what comes next. It needs help understanding the actual concepts behind the data.
Additionally, LLMs learn primarily from unregulated and unverified web content, which they propagate in their responses, making them prone to errors, contradicting information, and biases.
LLMs are limited to the knowledge in their training dataset. That’s why it’s critical for you to know which model is powering an AI application.
For example, OpenAI offers access to several models. You can see a complete list in OpenAPIs Models documentation, including its capabilities, when it was trained, and how it has evolved.
- If I’m a casual user with a free ChatGPT account, my ChatGPT experience is powered by the GPT-3.5 model. This model has knowledge captured in the training dataset before September 2021. That’s when OpenAI completed the machine learning part of development. The GPT-3.5 LLM hasn’t had access to events or discoveries since October 2021 besides what we’ve all input via ChatGPT interactions for fun.
- If I have a paid ChatGPT Plus subscription, my experience is powered by the GPT-4 and GPT-4 Turbo models, which completed training in April 2023.
Regardless of which LLM is working behind the scenes, none of the publicly available LLMs know anything about the internal workings of your business. It doesn’t have access to private, confidential, or proprietary information, including your intellectual property (IP). That’s the secret to making your business what it is. It’s what uniquely differentiates you from your competitors.
What’s an AI Hallucination?
So what happens when you ask an LLM a question and it doesn’t have the answer? It uses the patterns and relationships in the training data to return a response. When that answer is factually incorrect, it’s called a hallucination.
We asked ChatGPT about our CEO and founder, Seth Earley: "Who is Seth Earley?"
ChatGPT's answer included board-level positions, faculty appointments, awards, and credits from journals and books. These are all reasonable achievements for someone in Seth’s position. While some of the facts were true, ChatGPT fabricated other facts.
At best, hallucinations erode trust in AI systems and your business. At worst, incorrect information leads to business catastrophes like compliance issues, lawsuits, and jail time if customers lose money because they act on false information.
Mitigating Risk in AI Adoption
How can businesses ensure that their GenAI is reliable and trustworthy?
- Plan your AI strategy.
- Bring structure and context to enterprise information using IA.
- Reference your information sources to access your knowledge.
- Use the best features of an LLM: language processing and generation.
Planning Your Business’s AI Strategy
Planning an AI strategy can be daunting for businesses, but ensuring that your AI investments pay off is essential.
Start by imagining and defining what you hope to achieve with AI. Where can AI add value to your business?
Then, assess your organization’s readiness. A readiness assessment should evaluate organizational culture and alignment, information quality, and technical infrastructure.
Your next step depends on what you learn in your readiness assessment. Regardless of where you focus, select use cases that align with your business goals, have a high potential for ROI, and have information sets you can wrangle into compliance.
Information Architecture: Bringing Structure and Context to Enterprise Information
Businesses generate and capture vast amounts of data, content, and knowledge. Sometimes, information is structured; often, information is unstructured. Unstructured information is sometimes called "dark data" because it’s hard to find and lacks visibility. It ceases to have purpose or value if it's not findable.
Information architecture is the science, and sometimes art, of categorizing and labeling information so that it’s easy to find, retrieve, and use. IA works in systems that collect digital body language from users, interpret those signals, and return results that match.
We always approach IA projects with business objectives and the desired outcomes first and foremost. The success of any IA investment depends on how well-aligned it is with specific business needs.
We start by identifying and vetting use cases that support the desired business outcomes. Only then do we start building an information architecture using
- taxonomies,
- detailed vocabularies, and
- business ontologies with only enough detail to address the use cases
A well-designed IA is easy to extend as you identify new business use cases.
Why AI Needs IA
To make enterprise knowledge accessible through a conversational interface, you need a solid information architecture that enables the system to capture digital body language and match those signals to the most relevant content.
Search facets are an excellent example of an IA responding to user interactions. When you browse our blog, you can filter the content to remove instances that don’t meet your area of interest. In the following image, we send a digital signal indicating we want content relevant to knowledge engineering solutions.
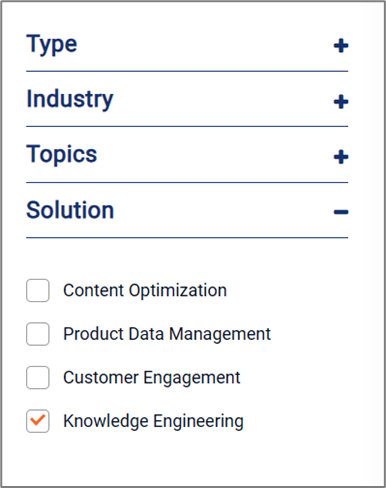
These filters correspond to the IA we use to classify our blog content in our backend systems. The search mechanism can return the most relevant information and remove what we might otherwise perceive as noise.
IA delivers the same benefits for AI solutions. AI works better when it understands the context and can disambiguate concepts based on the IA.
Context: How IA Provides Insight into Business Information
IA consists of all the taxonomies in an organization, along with the relationships between those taxonomies. It connects information across disparate information systems.
Let’s consider the business operations of an industrial distributor. This distributor carries products from several manufacturers. The manufacturers design products to operate in specific operating environments by people who know how to use them in companies that perform industrial jobs. Information is created in every interaction with manufacturers, customers, internal departments, and employees.
The following taxonomies help this distributor organize and find their diverse types of information.
When we add relationships among the taxonomies, we see how information is related across the enterprise.
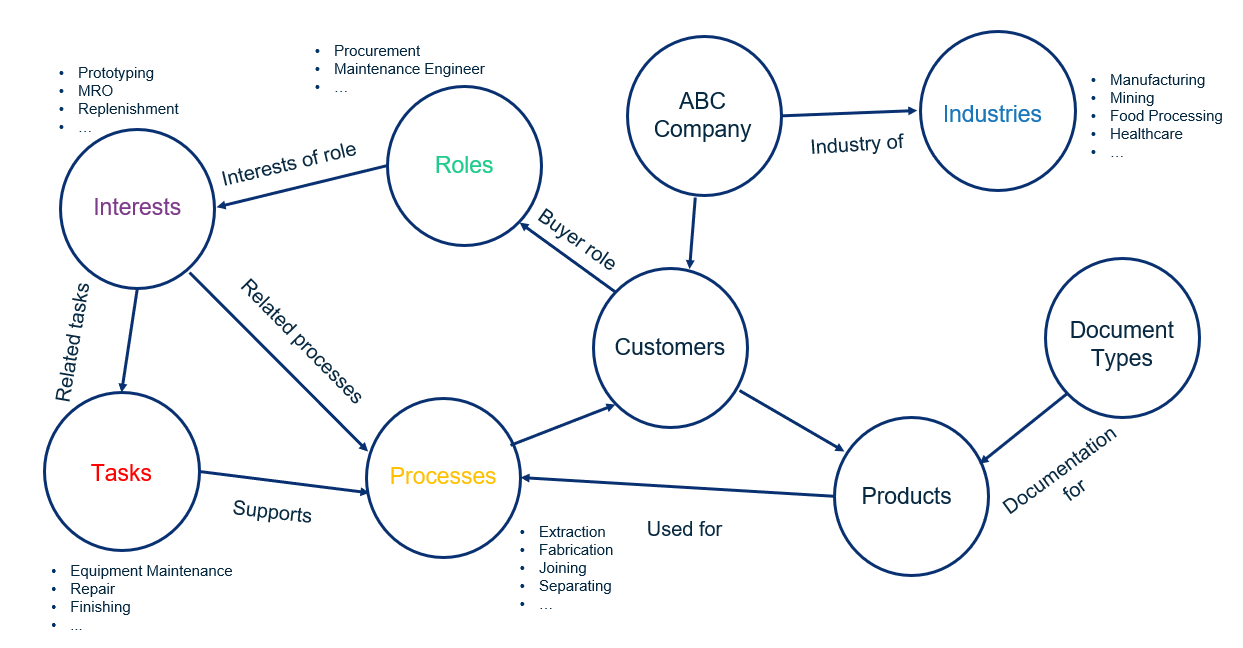
With the relationships in place, we can address more complex information needs in the business:
- How do we appeal to an engineering role with different interests than a procurement manager?
- Which customers and roles within those companies will be interested in a new product offering?
- Is the product designed to work in a rugged or marine environment?
Business Ontologies: How to Create an IA-Based Reference Architecture
A business ontology, like the one shown before, forms a reference architecture for business data and content by
- Providing a shared language
- Facilitating data integration
- Enabling semantic search
- Supporting knowledge management
- Promoting interoperability
The results include improved data quality, efficiency, and decision-making across the organization.
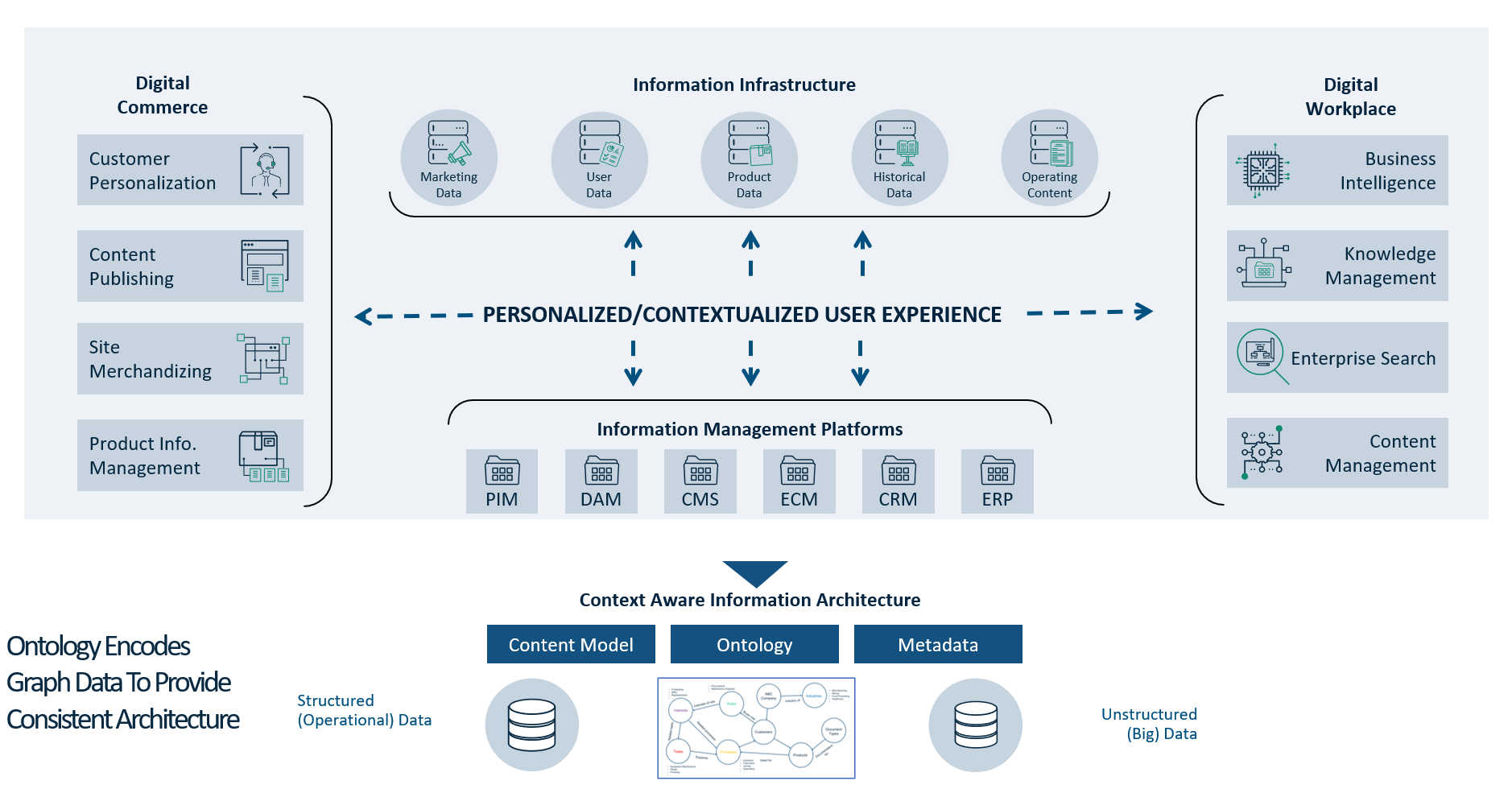 When the ontology is populated with data, it’s called a knowledge graph.
When the ontology is populated with data, it’s called a knowledge graph.
Ground Truth: Referencing Your Information Sources
Remember, LLMs learn from massive public data sets. They don't have access to your company's private information. But what if you need answers stored in your internal knowledge systems? Use retrieval-augmented generation or RAG.
RAG uses the LLM and GenAI capabilities to interpret user queries and generate a response. But instead of using public training data as the basis for an answer, it references internal knowledge sources and a carefully constructed IA. If the LLM can’t find the answer, it can prompt the user for more information based on the IA.
insert RAG image
RAG ensures that the AI system answers questions about policies, procedures, and brand guidelines correctly and consistently. You can also include report audit trails and traceability, making the AI mechanism clear, transparent, and explainable.
IA-Driven Applications in the Real World
Content Personalization
Content personalization is a form of recommendation. A recommendation engine takes what it knows about you and your digital body language and selects content to meet those characteristics.
| Slow-Changing Characteristics | Fast-Changing Characteristics |
|
Position or title Technical abilities Interest Company and its firmographics Customer journey |
Past purchases Responses to campaigns Searches Real-time digital body language like click paths |
Ontologies improve personalization by aligning the user and content characteristics.
That’s what the ABIe chatbot (Allstate Business Insurance Expert) did for Allstate Business Insurance. While that bot didn’t use an LLM, its information architecture powered a solution that led to successful business outcomes. Implementing a RAG-based system to access the information is straightforward.
Field and Call Center Support
Field technicians and call center agents often search through information silos, multiple content formats, and customer data to fix customer issues or answer customer questions. Many are finding that ontologies improve the performance of their systems – especially in complex technical domains – even before generative AI existed.
Applied Materials saved $50M per year in field service costs after developing and applying an ontology to solve the problem. Because they first started with a well-designed AI, implementing a RAG-based system to access that content is straightforward.
Conclusion: Making Generative AI Work for Your Business
Information Architecture is a critical part of the success of AI applications. By organizing, structuring, and managing information effectively, IA enables AI systems to access, process, and use data efficiently, leading to
- accurate results,
- better decision-making, and
- enhanced overall performance.
As AI continues to advance and permeate various industries, the importance of IA will only grow, ensuring that AI applications are reliable, scalable, and adaptable in an ever-changing, data-driven world.
The organizations that focus on getting their knowledge, data, and content house in order will be ahead of the game and positioned to capture true competitive advantage in this fast-moving space.
